Use Cases
Materials R&D

Since 2010, we worked with research institute and industry to develop and patent light, robust and highly thermally conductive composite materials. They have applications in CERN beam intercepting devices, such as LHC collimators, as well as for society (thermal dissipation systems, aerospace, nuclear & fusion).
Graphite and Diamond based composites
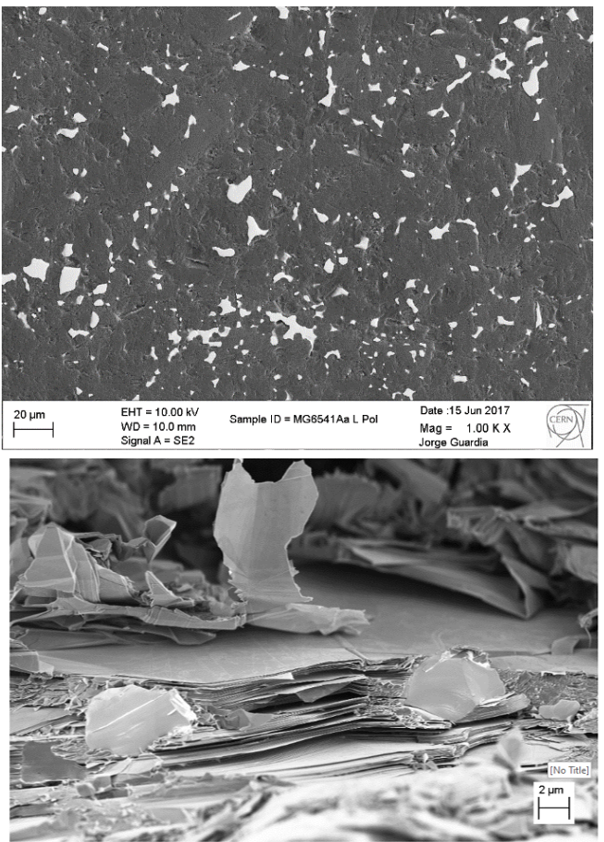
Molybdenum-Graphite
Molybdenum-Graphite (MoGr) has a graphitic matrix, with molybdenum carbide reinforcements. Its thermal conductivity is two times higher than copper, for a density three times smaller. Because of its good electrical conductivity and thermal-shock robustness, it is the baseline solution installed in the LHC primary collimators. In the LHC, MoGr is also employed in secondary collimators, in this case with a Mo coating to further boost its electrical conductivity.


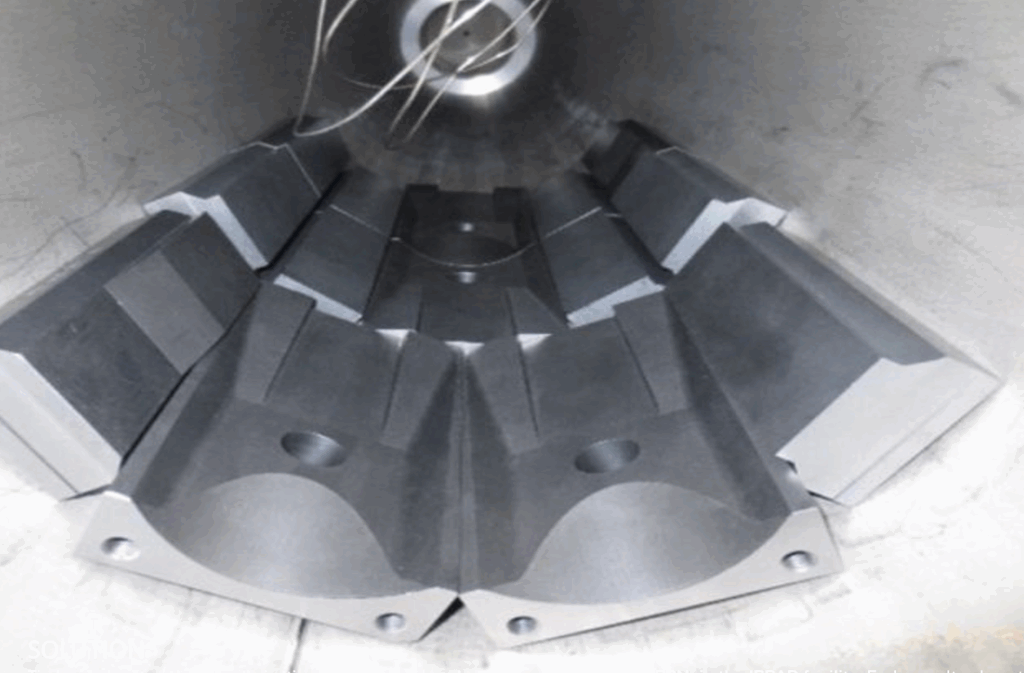

Chromium-Graphite
MoGr is very performant, but it comes at a high production cost. In order to decrease the production cost, while achieving similar thermophysical properties, we developed Chromium-Graphite (CrGr), which can be sintered at lower temperature.
CrGr is being investigated through EU-funded projects (I.FAST, EPITA).


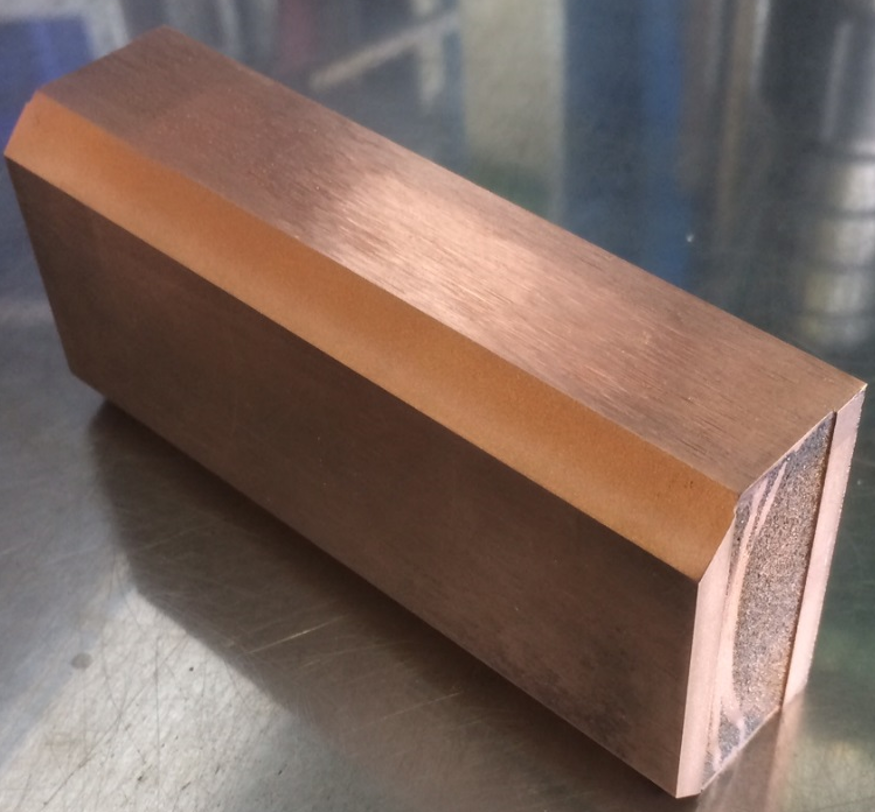
Copper-Diamond
Copper-Diamond (CuCD) is a medium density (5.4 g/cm3) composite with good robustness to particle beam impact. The combination of its two phases, the copper matrix and the diamond reinforcements, maximizes its thermal conductivity. It is considered a higher-robustness option, compared to the tungsten baseline, for LHC tertiary collimators.




FIND OUT MORE
Keen to learn more about our activities?
Find out what the Engineering Unit can do for you.
